Patellar tendon pain (often called patellar tendinitis or patellar tendinosis) occurs when the tendon connecting your knee cap (patella) to your shinbone becomes inflamed and irritated. Patellar tendinitis is often called “jumper’s knee” because it occurs so frequently in sports like basketball and volleyball. It also affects runners due to poor lower extremity biomechanics during running.
Patellar Tendinitis symptoms include:
- Pain directly over the patellar tendon.
- The tendon is usually tender and swollen.
- Knee motion can cause “crepitus” (when you hear and feel a crunching or grinding sensation). This may or may not be painful. It’s usually felt under the tendon or the lowest part of the knee cap.
- Pain with jumping.
- Pain with kneeling.
- Pain when walking downstairs.
The initial course of treatment should include RICE, which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
- Rest. In this case, rest would indicate tapering down from your regular exercise activity and discontinuing running (for the short term).
- Ice. Apply ice to the painful area. The rule for icing is to apply ice no more than twenty minutes per hour. Do not place the ice directly against the skin, especially if you are using a gel pack style. A bag of frozen peas can be ideal. Individuals with poor circulation or impaired sensation should take particular care when icing.
- Compression helps to prevent and decrease swelling. Swelling can cause increased pain and slow the healing response, so limit it as much as possible.
- Elevation. Depending on your pain level and the amount of swelling present, this step may be more or less beneficial.
In this video, I demonstrate how to utilize a mobility/compression band as a self-treatment method for patellar tendinitis. Mobility/compression bands, such as the Rogue Fitness VooDoo X Bands or EDGE Mobility Bands, are a novel way to self-mobilize tissue either of the quadriceps or the patellar tendon. The use of a mobility band not only helps to mobilize the tissue, but it affects blood flow to the area and speeds up healing. A mobility band also helps to reset some of the receptor cells in the muscle tissue which cause excessive muscle tightness.
As demonstrated in the video, start by applying the mobility band just below the tibial tuberosity, and then over the patellar tendon to the base of the patella. Next, perform the seated knee extension and then the squats. Typically, the mobility band will only be in place for one to two minutes. If you experience numbness or tingling, please discontinue the treatment. (If you suffer from any form of blood clotting disorder or are on blood thinning medications, I would advise against utilizing mobility bands for any type of deep compression.)
In addition to utilizing the mobility band, I often find that it’s critical to improve general tissue mobility. I recommend stretching and mobilizing the tissues of the lower legs. Myofascial release of the quadriceps muscle is an important component in order to relieve the pain while reducing the pressure and tension through the patellar femoral tendon and joint. This is typically a very effective and important step as most will find pain relief from improving quadriceps mobility. I tend to utilize the foam roller for the larger part of the quadriceps.
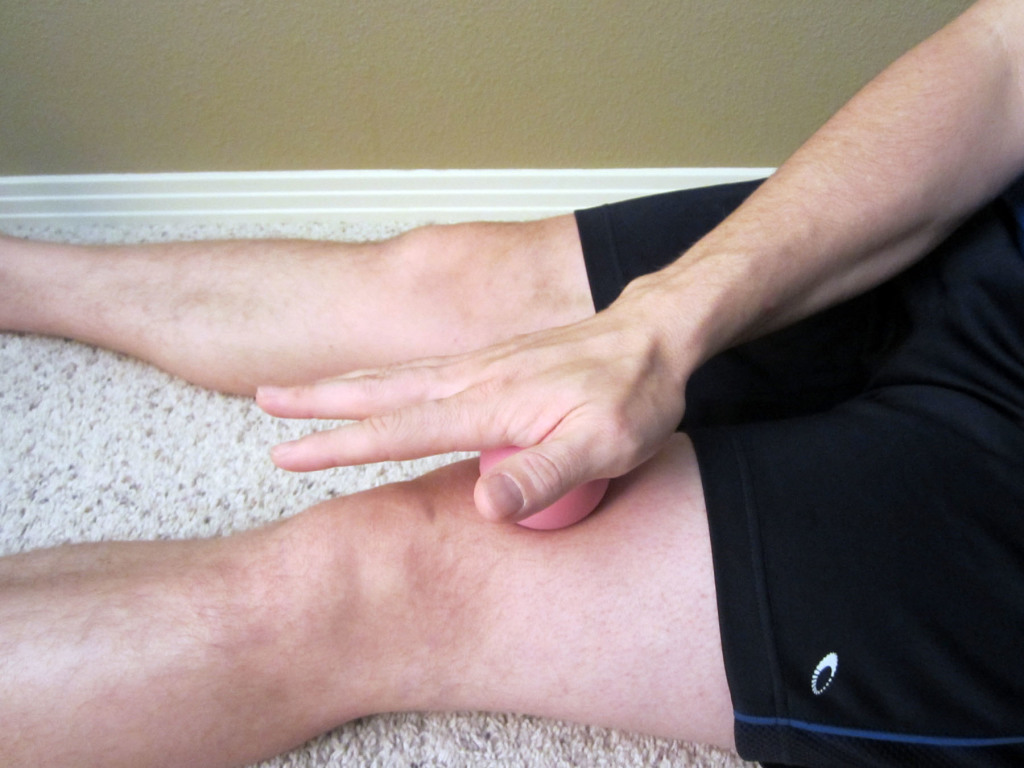
I also use a tennis or lacrosse ball to aggressively work the tissue above the patella. You can use your hand to press the ball in and work it around the tissue. To use the weight of your leg for a more aggressive mobilization, place the ball on the ground and mobilize the tissue with your leg on top of the ball.
For additional helpful tips and tricks on treating knee pain, please refer to my guest post for the Marathon Training Academy, How to Self-Treat Runner’s Knee. Much of the advice and training recommendations are also relevant to treating patellar tendinitis.
Have you tried using a mobility band before to treat patellar tendinitis? If so, what was your experience like? Please leave your comments below.
Looking for that exercise or book I mentioned in a post? Forgot the name of a product or supplement that you’re interested in? It’s all listed in the Resource Guide. Check it out today!
If you have a question that you would like featured in an upcoming blog post, please comment below or submit your question to contact@thePhysicalTherapyAdvisor.com. Be sure to join our growing community on Facebook by liking The Physical Therapy Advisor!
