Mobility bands (like the VooDoo Floss Band) are gaining in popularity as a self-treatment tool particularly among the athletic population. There are many brands manufacturing mobility or floss bands with most of them being very similar. Most mobility bands utilize a long piece of thicker elastic latex rubber to compress tissue in or around varying locations. Other brands (like the CTM Band) have made innovations to the more traditional style band which allows for a more aggressive mobilization into the soft tissue. (“CTM” stands for compression, tension, and movement.)
Reasons why you may choose to utilize a mobility band include:
- Pain modulation.
- Decrease myofascial type pain from muscle spasms and trigger points.
- To improve range of motion of a particular joint or tissue.
- To decrease edema and swelling.
- To reduce blood flow as part of a workout strategy such as blood flow restriction (BFR) training.
- To improve blood flow as part of a treatment OR as recovery/rehabilitation strategy in order to reduce edema or swelling in an injured area.
If you suffer from any form of blood clotting disorder or are on blood thinning medications, I would advise against utilizing mobility bands for any type of deep compression.
Presently, there are few research studies on the effectiveness and efficacy of utilizing mobility bands. However, there is a lot of antidotal evidence including my own.
What we know from the existing research is that “flossing” appears to have the most impact on ankle mobility and performance. In particular, short-term increases in ankle dorsiflexion mobility can have positive effects on activities (such as squatting and single-leg jump performance) and reduce ankle pain.
Present studies investigating the effect of flossing on the shoulder and elbow joints are yet to show significant improvements in mobility or power. However, increases in elbow mobility were noted in tennis players that had an existing mobility restriction.
The exact mechanism of action on how and why mobility bands work is still under debate. The general feeling is that depending on the intended use of the mobility bands, there are likely multiple mechanisms of actions. One or more of the mechanisms are likely being emphasized to produce the desired effect. My thought is that there are three major systems affected when utilizing mobility bands: circulation (blood flow); fascial (mobilization); and neuromodulation (improved range of motion through a nervous system response).
Blood Flow
Blood flow is affected because of the amount of compression provided by the mobility band. An immediate effect on the tissues will occur. This happens when the mobility band is applied (restricting the blood flow), and when it’s taken off (allowing for a rush of blood to the area).
This can have two positive, yet different effects: to decrease swelling and to cause nutrients to be delivered to the affected tissues. If the mobility band is used over an edematous (swollen) area, then the mechanical compression from the mobility band can help to decrease the swelling. To enhance the effects of the compression, all one must do is repeatedly move the compressed area through a normal range of motion. This combines the body’s natural muscle pump with mechanical compression while more swelling maybe eliminated. This is a short term effect as the mobility band should only be applied for 60-90 seconds at a time. (This technique is probably not suitable for highly edematous areas or those who suffer from lymphedema.)
As the mobility band is removed, the body’s immediate reaction is to restore blood flow which can cause hyper perfusion of the tissues. This hopefully will cause additional nutrients to be delivered via blood flow into the affected tissues.
Fascial Mobilization
Another theory on how mobility bands work is via fascial shearing. By adding a compression force to a tissue and then sliding it back and forth, one creates a type of “tack and floss” motion that seems to affect soft tissue and fascia. This is effectively a method of self-fascial mobilization.
Compressing muscle groups and taking them through their range of motion creates a flossing effect (which is where the term VooDoo flossing came from) between individual muscles. Compressing the fascia while flossing the tissues (by moving the extremity back and forth) may break up adhesions in the fascia that exist. This will allow for better range of motion and movement while reducing pain by addressing myofascial restrictions.
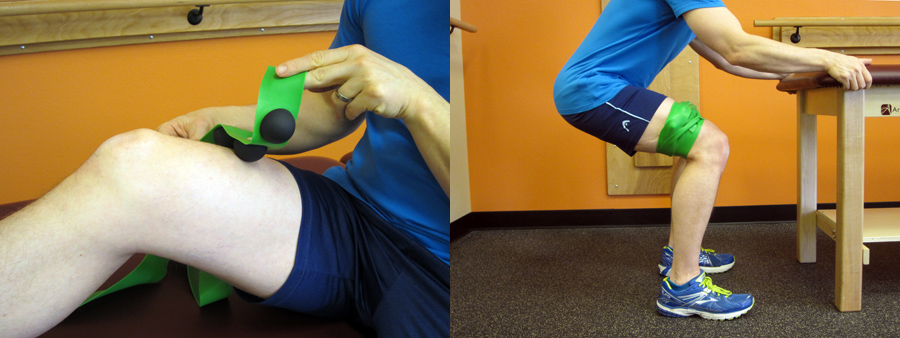
The CTM Band has taken this concept and added small rubber knobs within the band to increase the intensity of the flossing. Depending on how the knobs on the band are positioned, this creates a more pin point tack and floss scenario. This particular band can be highly effective for muscle groups in the calf, quadriceps, and hamstring area. Use code MTA15 for a 15% discount. (CTM Band techniques are not typically performed during the acute phases of recovery. They are more for prevention /pre-hab or to be used during the sub-acute or chronic phases during rehabilitation/recovery.)
Along with the tack and floss theory and depending on where the mobility bands is placed (like over a knee or ankle joint); one may produce a significant enough compression force over a joint with the mobility band that it creates a distraction force. This may create extra room in the joint capsule. Mobilizing a joint with the VooDoo Floss Band allows that particular joint’s full range of motion (without restrictions). In this case, there is an actual mechanical force affecting tissue length and/or mobility. This could have a mechanical “mobilizing” effect if the capsule was tight, but it could also be affecting joint mechanoreceptors (neuromodulation).
Neuromodulation
By positioning the mobility band over a joint to cause a distraction force over the joint and within the capsule, thereby allows for improved alignment and freedom of motion within the joint. This can have a neuromodulation affect over the joint which allows for improved range of motion. Although this can be a mechanical change, it may also be a neuromuscular change where joint mechanoreceptors are activated in a positive way. This can allow you to more freely utilize the extremity that you applied the mobility band to. Neuromodulation may also be achieved just through the unique stimulation caused by the band activating neuromechanoreceptors. The mobility band likely has multiple effects at once; more research needs to be done.
How to Use a Mobility Band
When using a mobility band, you generally wrap it toward your heart. The goal is to create a large compression force around the restricted joint or tissue. To achieve this, wrap the mobility band starting 2-3 inches below the area you want to treat. Aim to finish wrapping about the same distance above the treatment location. While wrapping, overlap about half the width of the mobility band. For mobility, a stretch of around 50-75 percent can be applied to the mobility band at the area you are treating. If you have any leftover band, additional compression can be applied by making an “X” over the treatment area.
Once the mobility band has been applied, you can try moving into the position causing restriction or by moving the joint or limb in all possible directions. There are guidelines for how long to keep the mobility band on. A general rule is to aim for around 1-2 minutes.
The application of the mobility band is going to compress the underlying tissues. However, care must be taken to not over compress or injure tissues. Discontinue use if you begin to feel the following:
- You begin to feel numbness or pins and needles (a sensation of uncomfortable tingling or prickling).
- You suddenly feel claustrophobic.
- You are losing volitional control of the extremity.
- You are experiencing increased pain or instability within a joint.
The mobility band should only be applied on the extremities. It should not be applied over your trunk area or any acute injuries including fracture sites, blood clots, wounds or any tissue areas that may be extremely sensitive to compression. Do not utilize if you have any medical reason not to utilize this technique. Common sense should always be utilized when using mobility bands as a treatment modality. If you’re not sure, then please speak to a medical practitioner prior to utilization. If you suffer from any form of blood clotting disorder or are on blood thinning medications, I would advise against utilizing mobility bands for any type of deep compression.
More specific instructions and examples on how to and why you may want to utilize a mobility band as part of a rehabilitation protocol (or even just to aid in recovery after longer runs) are covered in the Resilient Runner Program, which is designed to help YOU meet YOUR training goals by insuring you have the tools to avoid injury, recover quickly, and train at a peak level.

What’s Inside the Resilient Runner Program:
- Guidance on preventing and self-treating common running related injuries, including Hip Flexor Pain, Runner’s Knee, IT Band Syndrome, Piriformis Syndrome, and more!
- Specific guidelines on when and how to return to running after experiencing an injury.
- Rehabilitation guides with step-by-step photos demonstrating recommended exercises.
- Step-by-step instructions on how to apply Kinesiological tape.
- Downloadable podcasts, videos, and more!
If you’re tired of ongoing aches, pains, and injuries, learn how to become a resilient runner so that you can continue to train and compete in order to meet your goals!