You may have heard that if you suffer from low back pain (LBP) that you need to work your “core” muscles, but what if you suffer from neck pain (cervicogenic pain) and/or headaches? Well then yes, you would need to work the core muscles of the neck. Like the lumbar spine, the neck also has a group of core muscles that are specifically designed to insure proper cervical segmental stability and to maintain proper head posture. When weakness and dysfunction are present within this group of muscles, there is often ongoing neck pain that can lead to headaches.
Muscles of the cervical neck “core” include the deep neck flexors and deep neck extensors. Most people don’t know the names or how to spell these rarely talked about muscles. For those who like the nitty gritty details, the deep neck flexor muscles include the longus colli and longus capitis. The deep neck extensor muscles include the multifidus and the semispinalis cervicis. The sub occipital muscles (including the rectus capitus posterior major and minor) and the obliquus capitus superior and inferior also play a role in cervical stability. These muscles as a group make up the core muscles for the cervical spine.
When classifying muscles, and especially the cervical muscles, it can be useful to think of them conceptually as global movers and local stabilizers.
Global movers are involved in the generation of torque and produce movement. They function more like a light switch, either moving your head or not. When dysfunctional, there are spasms, pain, and a restricted range of movement.
Local stabilizers are the deeper muscles that control segmental movement and neutral positioning of a joint and the head. Their activity is tonic (always on). It’s like a light switch that is always on, but with a dimmer controlling the intensity. Local stabilizers operate at much lower levels of contraction for long periods of time. Dysfunction in the local muscles results in the inhibition of muscle function, delayed timing or recruitment of when the muscle is stabilizing which causes loss of segmental control and poor cervical vertebral joint positioning. This is often associated with chronic neck pain and headaches as well as muscle spasms in some of the larger muscles (such as the upper trapezius) as it attempts to compensate for the underlying muscle inhibition.
The neck presents a unique challenge of both mobility and muscularly speaking. It requires intricate muscular control to balance the weight of the head in space. The neck also moves the head through a large range of motion available; all while positioning it accurately to allow us to use our senses (sight, smell, hearing, and taste) most effectively.
Mobility and stability are both vitally important to how the neck functions. This is why the deep segmental stabilizing muscles are extremely important. These deep core muscles (also known as the “inner unit”) have been shown to weaken in the presence of neck pain or injury regardless of the cause. As part of a compensation pattern, one will often find that the prime mover muscles at the front of the neck, called the SCM (sternocleidomastoid muscle), become overactive trying to protect the neck.
Unfortunately, this creates excessive shear and compression forces on the neck which brings the head forward into the poking chin posture. This dysfunction pattern tends to persist even when the pain subsides unless properly retrained. This may explain why so many people experience recurrent episodes of neck pain. Discover why it’s important to insure proper cervical core strength in order to not only alleviate neck pain and headaches, but also to prevent them from reoccurring.
Most of the time neck pain is mechanical in nature. This means that there is a structural or mechanical issue affecting proper motion in the neck leading to either neck pain or headaches. Since the trigger is mechanical (starting or worsening with certain movements), it can just as easily be reduced or eliminated if the correct movements can be initiated. Mechanical neck pain is often experienced as cervical pain, headache pain or other correlated pain patterns in your upper back and down your arms (even to your fingers).
Neck Pain (Cervicogenic Pain) Symptoms include:
- Pain in the front of your head, behind your eyes or side of your head.
- Pain which begins from your neck that extends between your shoulder blades and upper shoulders.
- Pain which is exacerbated or changed by certain neck movements or neck positions.
- Pain which is triggered by pressure applied to the upper part of the neck near the base of the skull (known as the sub occipital area) or in the upper trapezius area.
- Pain down one or both arms. It can be felt as far as your fingers.
- Stiff neck.
- Altered or blurred vision as well as nausea, vomiting, and/or dizziness.
Potential Causes for Cervicogenic Headaches
There are plenty of reasons why one might develop neck/cervical derangements or dysfunction. Examples include: motor vehicle accidents; sports; falls; sleeping on a poorly fitted pillow; poor posture; and carrying items that are too heavy (such as a backpack). Chronically sustained non-symmetrical postures, stress, and a sedentary lifestyle are also potential causes.
The actual pain generating structures of the neck (listed below) vary wildly and can be difficult to pinpoint.
- Nerve related injury or pain
- Muscle spasms
- Trigger points
- Facet joint dysfunction
- Cervical mal-alignments
- Cervical disc issues
- Postural dysfunction
Cervicogenic pain and headaches tend to be more common in women than men. In general, women experience this due to minor anatomical differences. Men tend to have muscular necks. Women tend to have longer more slender necks with less muscle to provide support to the head (meaning that there is less muscle strength for support).
Treatment for Neck Pain (Cervicogenic Pain) and Headache Pain
Research suggests the most effective management of neck pain conditions include both manual therapy (hands-on mobilization) and manipulation with specific exercises. If you have to choose one or the other, I find that a correctly designed and implemented exercise program to be the most effective over the long term.
The first step to designing a treatment plan is by identifying a pattern to the pain.
Which head motions change or alter your neck or headache pain? Does the pain get worse or does it improve when you turn your head? What happens when you look up, look down, slouch or sit up straight? What happens when you repeat this movement?
Determine how your pain responds. This is also known as establishing a directional preference. You might be moving in the wrong direction if the pain spreads away from the spine and down into the upper back or arm. Stop that particular movement, and try the opposite direction.
In my experience, most episodes of cervical pain and headaches tend to respond better to cervical extension biased movements and improvements in posture. Gaining extension in the thoracic spine is also critical to treatment.
In order to determine if extension biased (cervical retraction or extension) movements help you, I recommend starting with this exercise (as shown below). Sit up straight, and retract your chin straight back. Repeat 10-20 times.
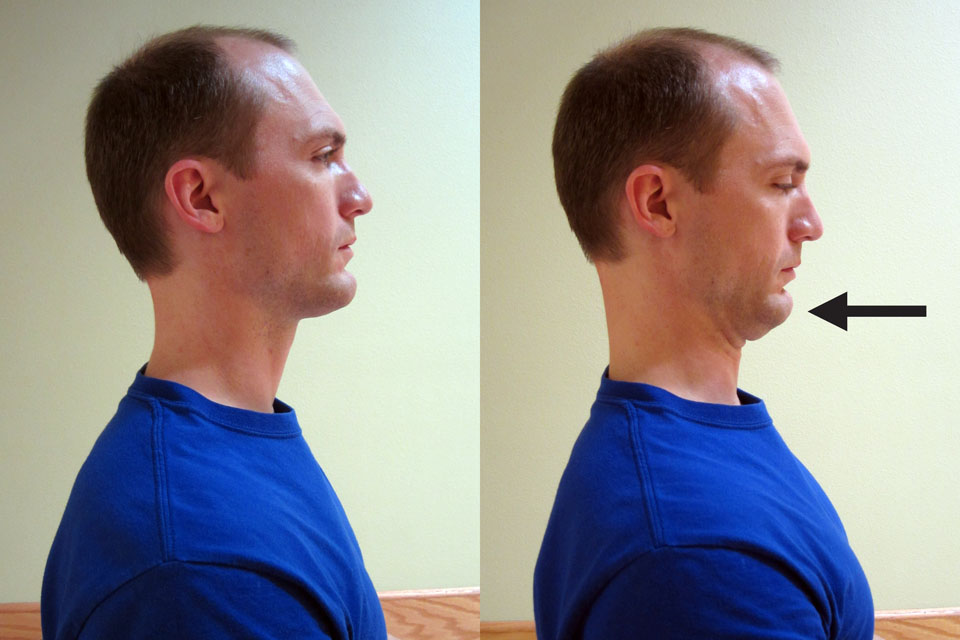
Carefully monitor symptoms for peripheralization or centralization. The rule of thumb for movement: If the pain worsens by spreading peripherally down the arm into the hands, fingers, shoulder blade/upper back or the headache gets worse, then the condition is worsening (peripheralizing). Stop that activity. If the pain centralizes and returns back toward the cervical spine, and the headache pain improves (even if the pain in the neck worsens slightly), then keep moving as the condition is actually improving.
If you are unable to help or change the pain in any way, then you may need assistance from a medical provider. For a thorough discussion and an excellent treatment resource, please refer to Treat Your Own Neck by Robin A. McKenzie.
Once you have determined a directional preference, then you can focus on the deep core and stabilizer muscles. For my initial neck core strengthening exercises, please refer to Deep Neck Flexion Exercises.
Once you’re able to engage the deep neck flexors, you can next progress into strengthening your scapulothoracic and postural muscles. Be sure you are engaging the deep neck flexors during these exercises to insure proper stability of the neck.
For the I’s, T’s, and Y’s exercises (as shown below), work up to holding each position for 30 seconds. Repeat 3 times. Keeping the correct posture and deep cervical flexor muscles engaged during this exercise is critical to engaging the full core of the neck.

Other Treatments for Neck Pain (Cervicogenic Pain) and Headache Pain:
- Focus on your posture. Poor posture is the bane of modern society. The most common example of poor posture is a forward head with rounded shoulders. This causes excessive muscular tension throughout the cervical spine, upper trapezius region, and mid-thoracic area. Over time, this leads to muscle weakness and dysfunction in the cervical spine and upper thoracic area. Proper posture allows for the optimal alignment of your spine. Neurologically speaking, this allows for your muscles to down regulate by reducing tension. Poor posture is almost always associated with muscle knots and trigger points. My Top 8 Stretches to Eliminate Neck, Upper Back, and Shoulder Pain is a downloadable .pdf file with my recommended stretches using foam roller exercises to address posture. These simple exercises (with complete instructions and photos) will help you to improve poor posture and can be performed at home.
DOWNLOAD NOW: My Top 8 Stretches to Eliminate Neck, Upper Back, and Shoulder Pain
- Manual Therapy. An osteopathic physician, physical therapist or chiropractor can use manual therapy techniques. This includes joint mobilization and manipulation which can be beneficial in reducing pain and addressing some of the mechanical causes. However, manual therapy is a passive treatment. For long term treatment and prevention, an active approach needs to be taken. I would encourage you to perform proper exercises to insure that you have adequate cervical and upper thoracic strength and mobility. Also, address any precipitating factors (such as poor posture).
- Massage. Although massage can be a form of manual therapy, it can also be thought of as separate intervention. There are many types of body workers that can utilize many different forms of massage or manual treatments. Many trigger points and muscle spasms will refer pain into the head (which causes the headache). It’s important to actively and physically address the muscle tension. This is the time to contact a massage therapist, body worker, physical therapist, athletic trainer or friend who is skillful in body work or massage to relieve the area in spasm. The specific massage technique to use will vary according to your preference. Massage techniques range from a light relaxing massage to a deep tissue massage or utilization of acupressure points. This can also be an effective prevention strategy.
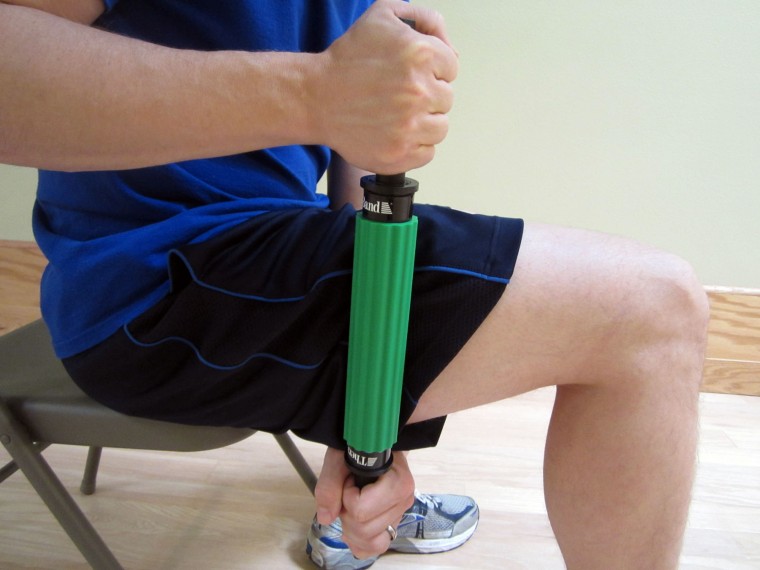
- Other self-mobilization tools. Many times, a friend or massage therapist isn’t available to assist when you need the help the most. A foam roller cannot effective reach places in the upper back or arms, so other self-mobilization tools may be necessary. You can get creative and use a tennis ball or golf ball, but I like a specific tool called the Thera Cane Massager. This tool allows you to apply direct pressure to a spasming muscle. When held for a long enough period of time, the Thera Cane Massager will usually cause the muscle spasms to release and provide much needed pain relief!
- Topical agents. Many topical agents can help to decrease and eliminate muscle spasms. They can also mediate the pain response helping to reduce neck pain or headache pain. You can apply a small amount of topical agent directly over the pain area if it’s accessible and not near your eyes. (Please use common sense). You may find that one product works better than another. Some of my favorite products in my medicine cabinet include: Biofreeze Pain Relieving Gel, Arnica Rub (Arnica Montana, an herbal rub), and topical magnesium.
- Magnesium bath. The combination of warm water with magnesium is very soothing and relaxing. Magnesium is known to help decrease muscle pain and soreness. Options include: Epsoak Epson Salt and Ancient Minerals Magnesium Bath Flakes. I find that the magnesium flakes work better, but they are significantly more expensive than Epson salt.
- Acupuncture. I am personally a big fan of acupuncture. It is very useful in treating all kinds of medical conditions. It can be particularly effective in treating headaches, muscle trigger points, muscle cramps, spasms, and pain as it addresses the issues on multiple layers. Acupuncture directly stimulates the muscle by affecting the nervous system response to the muscle while producing a general sense of well-being and relaxation.
- Medications. Medications can be an effective short term solution to headache pain, but I strongly encourage you to transition off of medications over time. In some cases, prescription medications may be used initially to help you tolerate the pain as you work toward prevention. Please speak to your physician regarding prescription options.
- Speak with your Physical Therapist (PT) or Physician (MD or DO). If you are suffering with neck pain and headaches, there are options. Please speak to your medical provider to determine if other causes are contributing to the problem. Physical therapy is very effective treatment for those suffering with neck pain and headaches. The American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) offers wonderful resources to help find a physical therapist in your area. In most states, you can seek physical therapy advice without a medical doctor’s referral (although it may be a good idea to hear your physician’s opinion as well).
Don’t give up hope! Neck pain and headaches can be difficult to manage, but with proper care, most of the pain can be cured or effectively managed. Begin by implementing one or two of these treatment tips, then assess how well they worked for you. If the technique helped, continue with it then implement another strategy.
If you suffer from neck pain and headaches, which treatments have worked the best for you? Please share below.
If you have a question that you would like featured in an upcoming blog post, please comment below or submit your question to contact@thePhysicalTherapyAdvisor.com. Be sure to join our growing community on Facebook by liking The Physical Therapy Advisor!