A hamstring strain, also known as a hamstring pull, is a relatively common injury that can occur in almost any sport: running, CrossFit, ice skating, and weightlifting. The injury typically happens when one of the hamstring muscles (which are located in the posterior or back of the thigh) become overloaded. This causes a strain or small tear of the muscle and a complete tear in severe cases. The pain is typically located in the back of the thigh near the site of injury. This area can range from the back of the knee to the buttock area (specifically near the bones of the pelvis you sit on called the ischium). Discover the factors that increase your risk of straining your hamstring and learn how to self-treat this condition.
The strain most commonly occurs during running or jumping (in particular during sudden movements or when quickly starting and stopping). However, you could just as easily pull your hamstring while weightlifting or working in the yard. The following factors increase your risk of straining your hamstring:
- Not warming up prior to exercise
- Tightness in the hip flexors or quadriceps muscles
- Weakness in the glutes/buttock muscles
Although hamstring strains are relatively common, they can be very debilitating. Depending on the severity of the sprain, you may have to discontinue your sport. A minor strain is classified as Grade I. Grade I injuries tend to be mild. With proper care and rehabilitation, the healing time can be shortened.
Grade II tears are partial ruptures. Grade II tears can often be rehabilitated, but the time frame for healing is longer.
A complete rupture is classified as a Grade III tear. Grade III tears may require surgical intervention. Severe Grade II and Grade III tears cause impaired muscle function and usually have associated bruising that occurs near the site of injury.
The course of treatment is dependent on the severity of the pain and the location of the injury. I recommend that you seek competent advice from a medical doctor, physical therapist or athletic trainer if you’re experiencing severe pain. A professional can assess the severity of the strain and address how to handle the injury.
Initial Treatment
For the purpose of this discussion, I will address a Grade I or minor Grade II injury. The initial course of treatment following the sprain includes RICE, which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
- Rest. In this case, rest would indicate tapering down from your regular exercise activity or any activity that involves using your hamstrings (bending over, walking uphill, squatting or activities involving hip extension or bending your knee).
- Ice. Apply ice to the painful area–typically the sooner, the better. The rule for icing is to apply ice no more than twenty minutes per hour. Do not place the ice directly against the skin, especially if you are using a gel pack style. A bag of frozen peas can be ideal. Individuals with poor circulation or impaired sensation should take particular care when icing.
- Compression helps to prevent and decrease swelling. Swelling can cause increased pain and slow the healing response, so limit it as much as possible. You can utilize a common ACE wrap. If you have a friend who is medically trained, many different taping techniques can also assist in decreasing swelling. Many physical therapists or athletic trainers can apply KT Tape, Rock Tape or Mummy Tape for you or you can find application techniques online.
- Elevation. Compression and elevation may not be fully possible if the injury is located higher into the buttock region. If there is swelling in the lower leg, then elevating the leg may be helpful.
Gentle Movement
During the acute phase, gently move the leg as you can tolerate. Don’t be aggressive with the movement. Walking is usually the best way to keep the area moving. Be sure to keep your steps shorter if you are experiencing pain. You may also try gently floating or walking in a pool as long as the pain does not worsen.
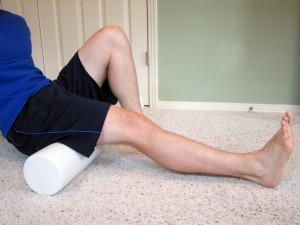
How to Self-Treat a Hamstring Strain/Pull:
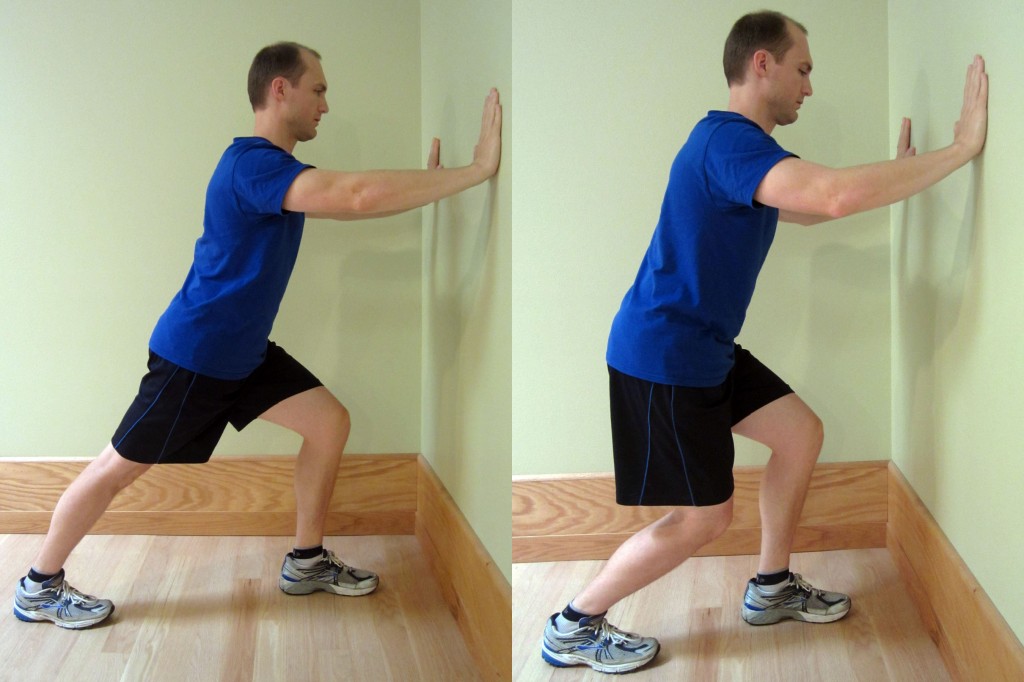
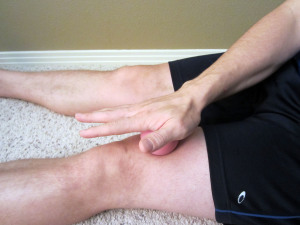
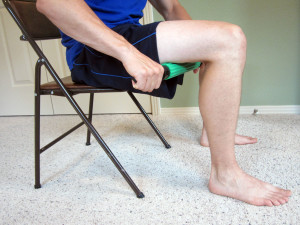
- Mobilize the fascia and muscle tissue. As you progress through the initial acute phase (typically 10 to 14 days), work on restoring normal pain free movement of the leg. Mobility issues and myofascial restrictions are very likely to occur following a hamstring injury. Along with tightness in the hamstring, you are likely to have tightness throughout the lower leg including the buttocks, quadriceps, IT Band or in the deep hip internal or external rotators. You may also have more spine tightness or pain due to altered movement patterns in the lower extremity. I recommend using a foam roller to address tightness in the lower leg. Care should be taken, and don’t roll too aggressively on the site of the injury. To learn how to use a foam roller, please refer to Foam Rolling for Rehabilitation. I also recommend using a Thera-Band Standard Roller Massager, which is very firm and allows for a deep amount of pressure. You may also utilize a tennis or lacrosse ball to mobilize the deeper hip and buttock muscles or to more deeply and aggressively mobilize the restricted areas appropriately.
- Stretch. As you progress through your rehabilitation, care should be taken when stretching the hamstring. I tend to utilize both mobilization and gentle stretching to help maintain hamstring and lower leg motion. Don’t let the hamstring become tight and restricted. Hamstring Rehabilitation Exercises demonstrate my recommended stretches, foam rolling, and self-mobilization techniques.
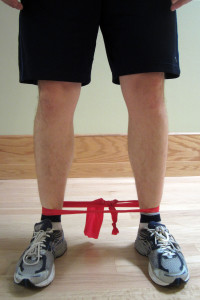
- Strengthen your glutes, hamstrings, and hip muscles. Weakness in the glutes, hamstrings, and hip muscles is common after injury and was likely a contributing factor to the injury itself. Strengthening of these muscle groups can help avoid future hamstring and even low back pain issues as well as reduce your risk of re-injury. Please refer to Hamstring Rehabilitation Exercises for additional exercises.
- Hydrate. The human body is primarily made of water, which is critical for all body functions. I highly encourage you to hydrate more frequently during recovery. Adequate water intake is critical as your body attempts to heal and flush out metabolic wastes. Dehydrated tissues are prone to injury as they struggle to gain needed nutrients to heal and repair. Dehydrated tissues are less flexible and tend to accumulate waste products. Keep steady supplies of nutrients going to/from the site of the injury. Try to avoid beverages that contain artificial sweeteners or chemicals with names you can’t spell or pronounce. Water is best.
- Start a supplement. A hamstring strain is typically associated with a specific event and an active inflammatory process typically occurs. I am a supporter of natural supplements and remedies. Many supplements include herbs which are designed to help reduce inflammation and support the healing response. My most recommended supplement to help recover from injury is CapraFlex by Mt. Capra. Essentially, it combines an organic glucosamine and chondroitin supplement with other natural herbs which are designed to reduce inflammation and support healing. CapraFlex can be taken long term or intermittently. Phenocane Natural Pain Management combines the following: Curcumin, an herb that reduces pain and inflammation; boswellia, a natural COX2 inhibitor that also reduces pain and inflammation; DLPA, an amino acid that helps to increase and uphold serotonin levels in the brain; and nattokinase, an enzyme that assists with blood clotting and reduces pain and inflammation. If you are taking blood thinner medication, please consult with your physician prior to taking these supplements.
Return to Activity
As your pain decreases and after your hip and hamstring range of motion has returned to normal, slowly start tapering back into your training routine. During this time, you remain at a higher risk of injury. As you continue working through your rehabilitation and your return to activity, implement the following strategies:
- Warm up prior to exercise. I recommend that you increase your normal warm up time. You should warm up at least 10 minutes in order to increase blood flow to the area. This allows for better mobility and also prepares the tissues for exercise. You can use a self-massage tool or a foam roller to roll up and down the hamstring as part of your warm up. If you perform hamstring stretches, be mindful that prolonged static stretching before exercise may worsen performance. Warm up exercises may include light jogging, bicycling, rowing or any activity to get the heart rate up and the blood flowing in the lower legs. Be careful when performing any movement that puts the hamstring in a stretched positon with speed or force.
- Cool down. After performing your exercise or activity, take the extra time to cool down and stretch. Focus on hamstring stretching as well as general lower extremity mobility stretches. Use the same self-massage tools as you did during your warm up.
- Initially avoid potential high risk activities. As your recovery progresses and you return to activity, initially avoid high risk activities that put the hamstring muscle under heavy load or a very quick load. Progress slowly. If an activity begins to cause pain in the hamstring, don’t push through it. Instead, stop and give your hamstring more time to heal prior to trying it again. You should be pain free before you progress the intensity of the activity or sport. Hamstring pulls have a high likelihood of re-injury if you rush the process.
- Regain full strength and motion before returning to sport. Before a full return to sport or activity is initiated, you should have full lower leg and hamstring mobility and strength without pain. If you continue to experience soreness or restriction, continue to work on your rehabilitation until the leg and hamstring have returned to normal. Then initiate a full return to activity.
If you’re not experiencing relief after two to three weeks of aggressively managing the symptoms, contact your medical doctor, physical therapist or athletic trainer for an assessment and help in managing the injury. The American Physical Therapy Association offers a wonderful resource to help find a physical therapist in your area.
Has a hamstring strain/pull ever sidelined you? Which treatment was the most effective for you? Additional discussion can help others to manage this condition more effectively. Please leave your comments below.
Looking for that exercise or book I mentioned in a post? Forgot the name of a product or supplement that you’re interested in? It’s all listed in the Resource Guide. Check it out today!
If you have a question that you would like featured in an upcoming blog post, please comment below or submit your question to contact@thePhysicalTherapyAdvisor.com. Be sure to join our growing community on Facebook by liking The Physical Therapy Advisor!
Disclaimer: The Physical Therapy Advisor Blog and its information is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute the practice of medicine or other professional health care services, including the giving of medical advice. No health care provider/patient relationship is formed. The use of information on this blog or materials linked from this blog is at your own risk. The content of this blog is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Do not disregard, or delay in obtaining, medical advice for any medical condition you may have. Please seek the assistance of your health care professionals for any such conditions.
 Running injuries that crop up during marathon training are a real bummer! Here’s part two of our Q and A with physical therapy doctor Ben Shatto.
Running injuries that crop up during marathon training are a real bummer! Here’s part two of our Q and A with physical therapy doctor Ben Shatto.